Published: April 21, 2024 | 9 mins read
Uric Acid Kidney Stones: Subtypes and Causes
Uric acid (UA) kidney stones are the second most common kidney stone type, comprising about 15% of the cases worldwide. Unfortunately, the number of UA stone-formers is on the rise. As always, the leading cause of this trouble is DIET.
However, if you think uric acid is the main culprit, you are missing the mark. Even people with normal uric acid levels can form this type if you have the one thing that increases your risk.
What’s that one thing?
Let’s find out in the following section.
CAUSES OF URIC ACID STONES
Three factors contribute to uric acid stone formation: low urine volume, urinary uric acid, and acidic urine.
Typically, uric acid can be dissolved in the urine. However, its solubility decreases when the urine becomes acidic (< 5.5 pH). That means uric acid crystallizes under an acidic urine environment. Interestingly, it dissolves six times higher at a urine pH of 6.5 compared to pH 5.3.
Four studies showed patients with uric acid stones have a urine pH below 6. A low urine pH caused uric acid stones even when the total uric acid excretion was normal. This proves that the primary culprit for this stone type is acidic urine. Uric acid alone won’t be a problem if you maintain a neutral urine pH (6.0-7.0).
Curious enough, what could be driving an acidic urine?
Often than not, metabolic syndrome and diabetes, which point to poor diet, cause this extra acidity.
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of risk factors, including the following:
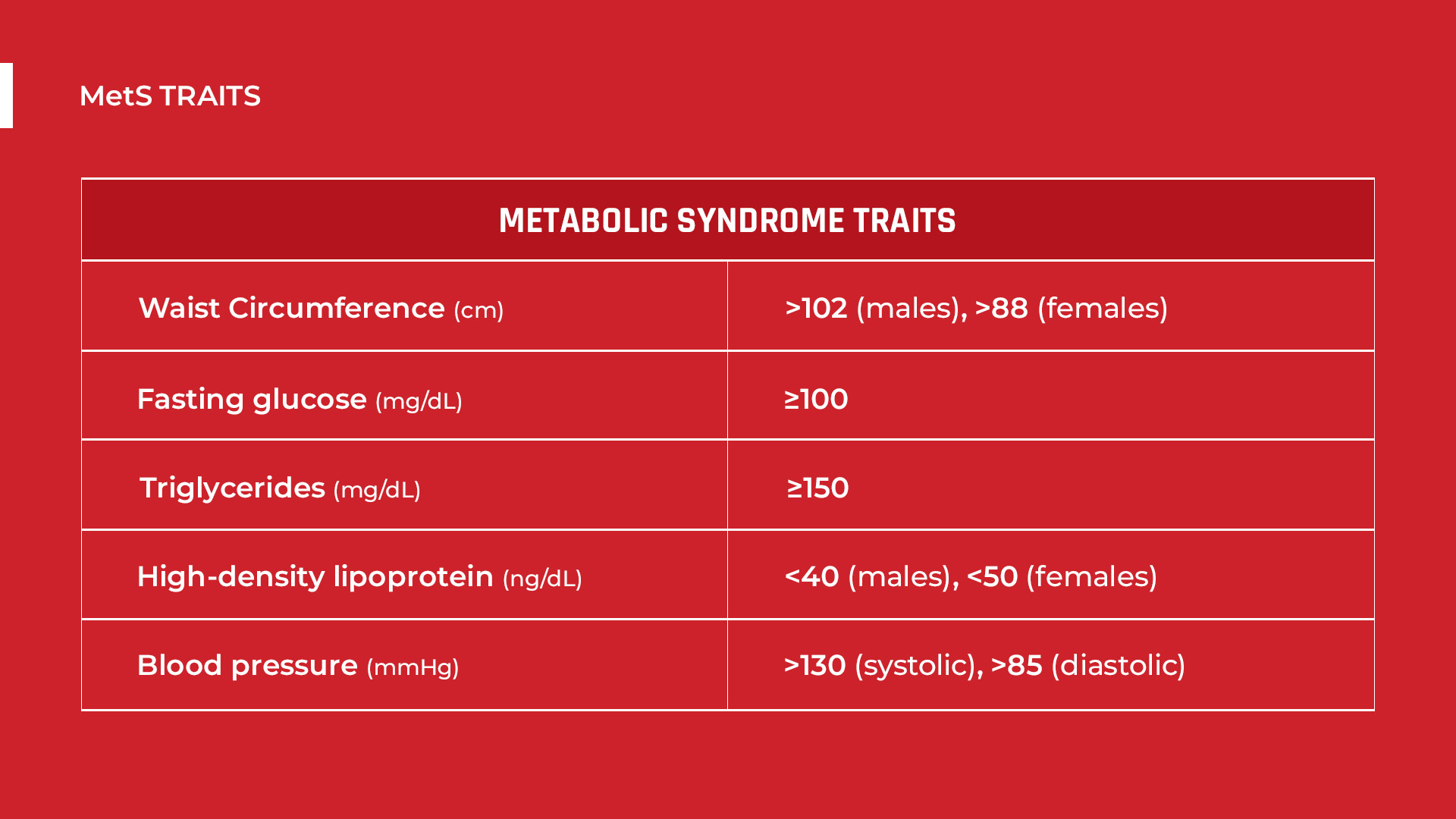
A study involving 5000 kidney stone-formers found that obesity and high blood sugar levels (fasting glucose over 100mg) result in acidic urine. This is due to decreased ammonium production in the kidney. Ammonium is an alkaline ion, so reduced levels can lead to acidic urine.
Meanwhile, hypertension and dyslipidemia (high triglycerides and low HDL) don’t necessarily lower urine pH. However, they can affect the blood vessels throughout the body, including the kidneys. This can lead to inflammation and constriction, which reduces urine output.
Also, inflammation can favor the formation of plaques (Randall’s Plaque) where calcium oxalate (CaOx) stones thrive. In that sense, hypertension and dyslipidemia are risk factors not only for UA stones but also for this other type.
Now that we understood the impact of metabolic syndrome, let’s talk about diabetes.
Diabetes
There are two types of diabetes. Type 1 happens when the immune system mistakenly destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The body can’t produce enough of this hormone, which is responsible for knocking on the cells to let glucose (sugar) in for energy. On the other hand, Type 2 is characterized by insulin resistance. The pancreas produces enough insulin, but the cells can’t recognize it, so glucose will stay in the blood.
Both Type 1 and 2 diabetes cause acidic urine because they alter how sugar is regulated in the body. Most of the time, they result in more sugar in the blood, which, as explained earlier, causes less ammonium production in the kidney. This makes the urine more acidic.
Lastly, what role does low urine volume play in this drama?
Low Urine Volume
As a general rule, if you don’t urinate often, stone-forming materials sit longer in your kidneys. It’s equal to giving them all the chances in the world to bind together, form stones, and trouble your life. So, you have to maintain proper hydration to prevent whatever stone type. When we say proper hydration, we mean drinking about 96 oz. of water daily. Drinking this much is a key point in your prevention plan
THE SUBTYPES OF URIC ACID KIDNEY STONES
Just like other stone types, uric acid kidney stone is also an umbrella term. There are different subtypes of it depending on how they distinctively form. Below is a comprehensive list.
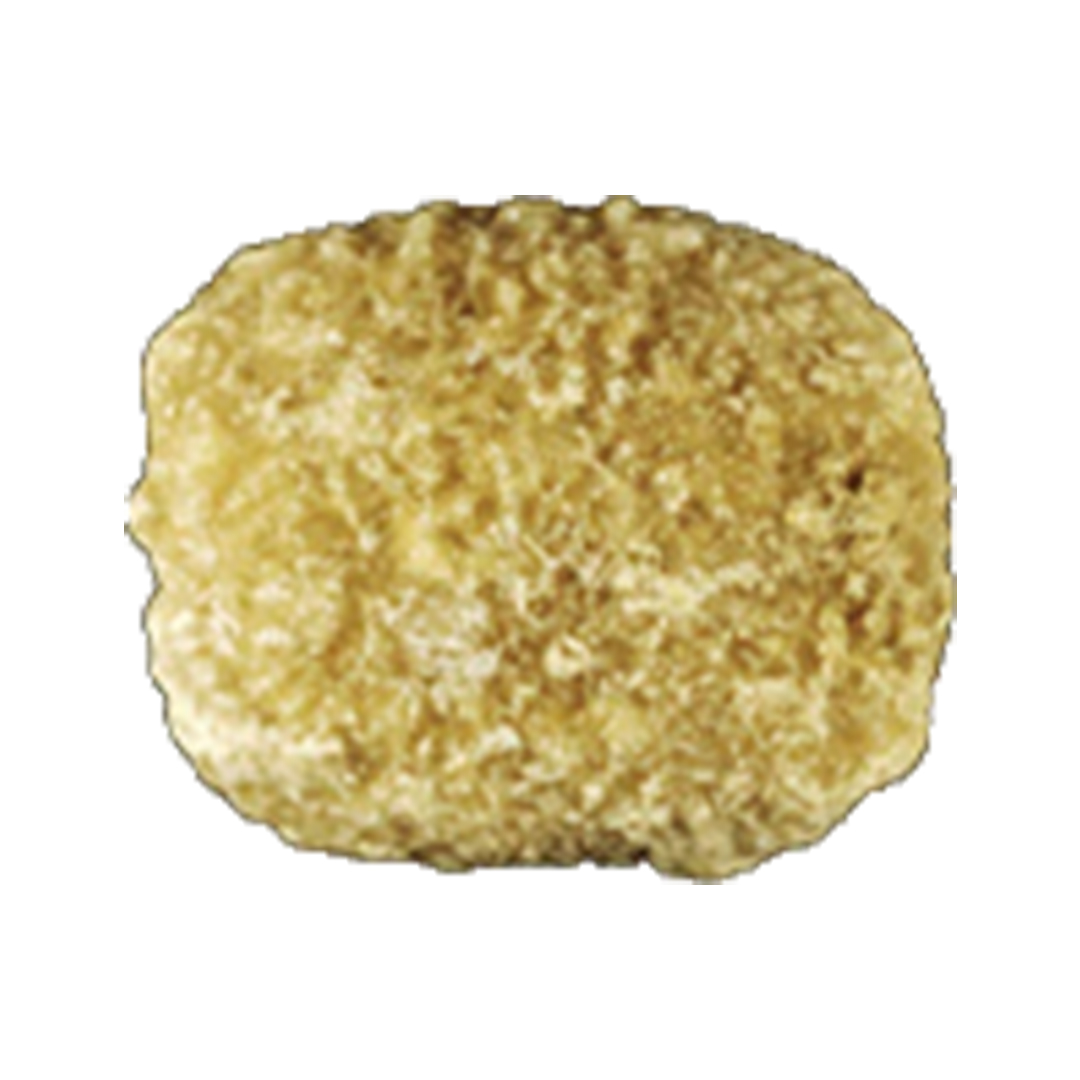
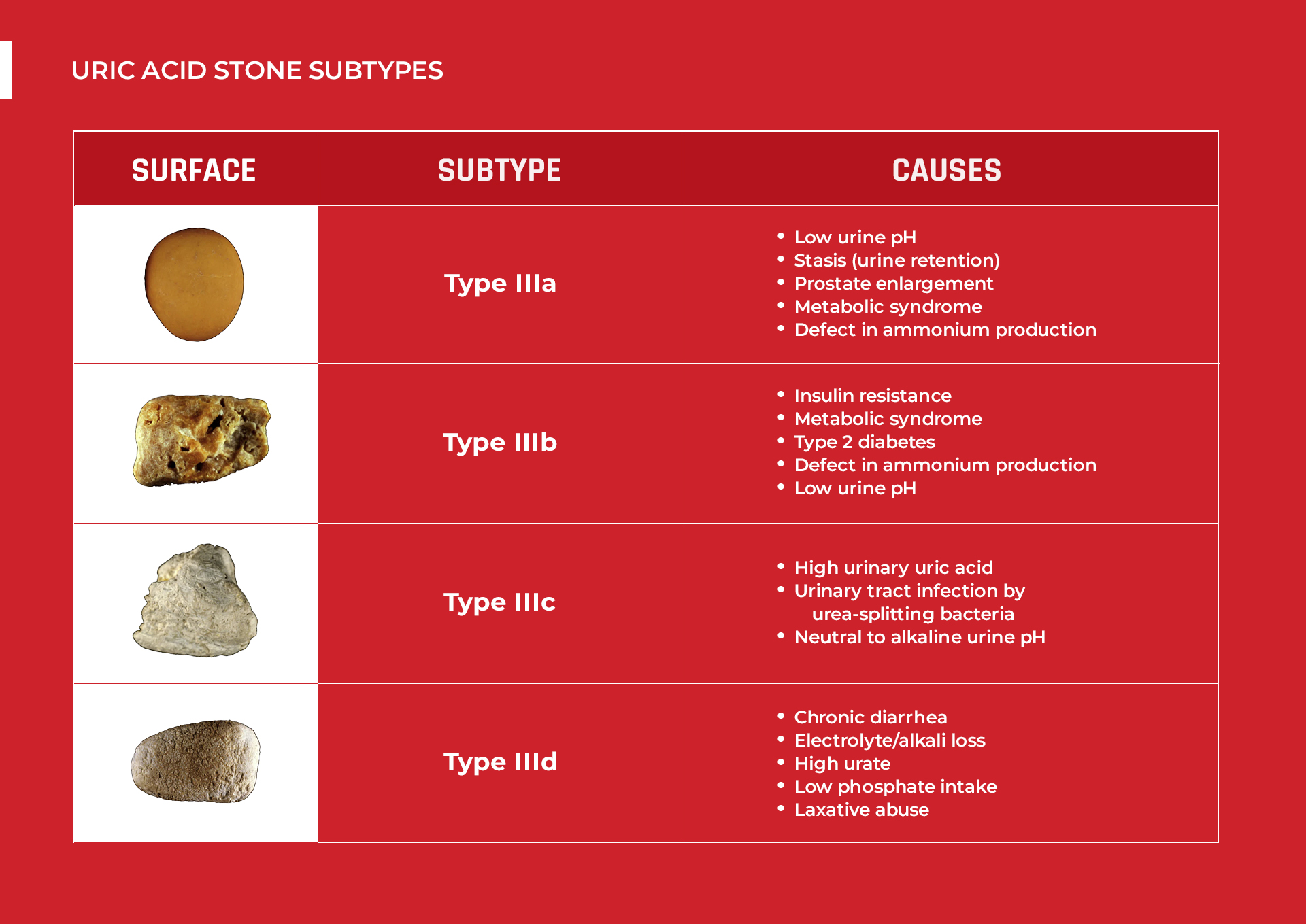
TYPE IIIa STONES
This type usually has the following characteristics:
- Has an even and smooth surface
- Typically orange, sometimes cream, ochre, or yellowish in color
Low urine pH, stasis (urine retention), prostate enlargement, metabolic syndrome, or defect in ammonium production are the causes of this type.
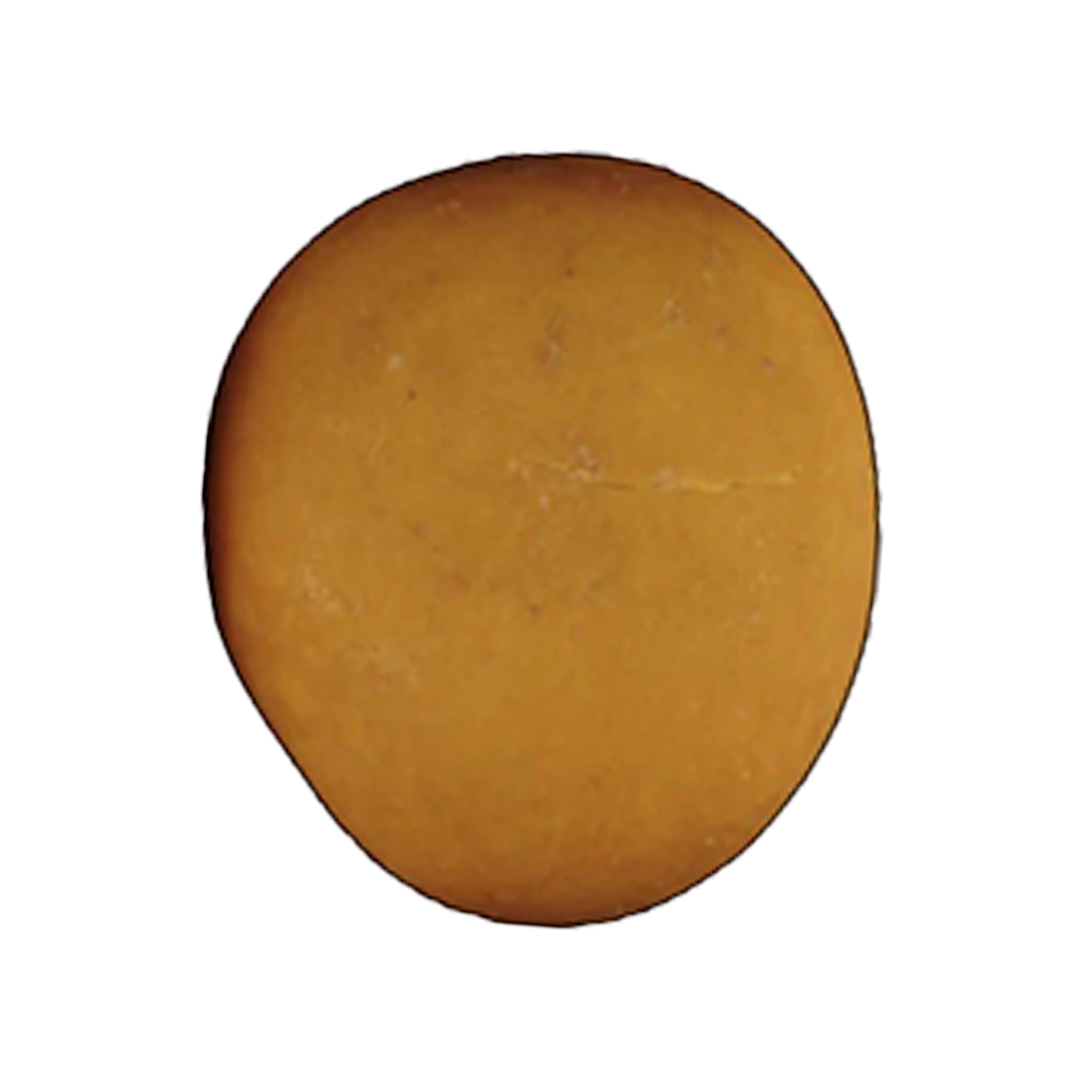

TYPE IIIb STONES
These stones are characterized as follows:
- Has an unevenly embossed surface
- Rough and porous in texture
- Beige to brown-orange in color
The leading causes of this type are insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, defect in ammonium production, and low urine pH.
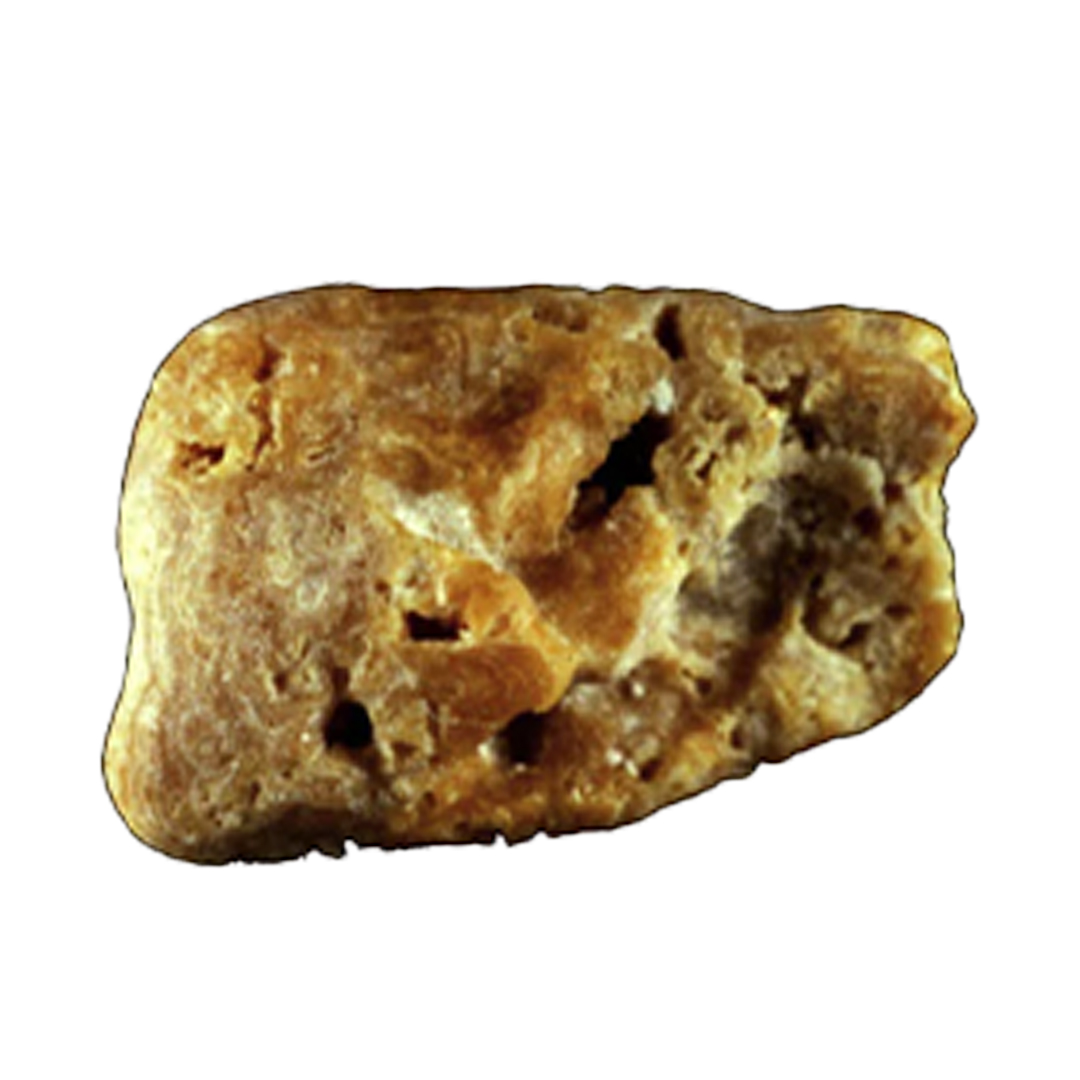

TYPE IIIc STONES
Type IIIc stones have these attributes:
- May appear slightly rough and locally porous on the surface
- Usually cream to grayish in color
These are caused by high urinary uric acid and urinary tract infection by urea-splitting bacteria. You can have this type even if your urine pH is neutral or alkaline.
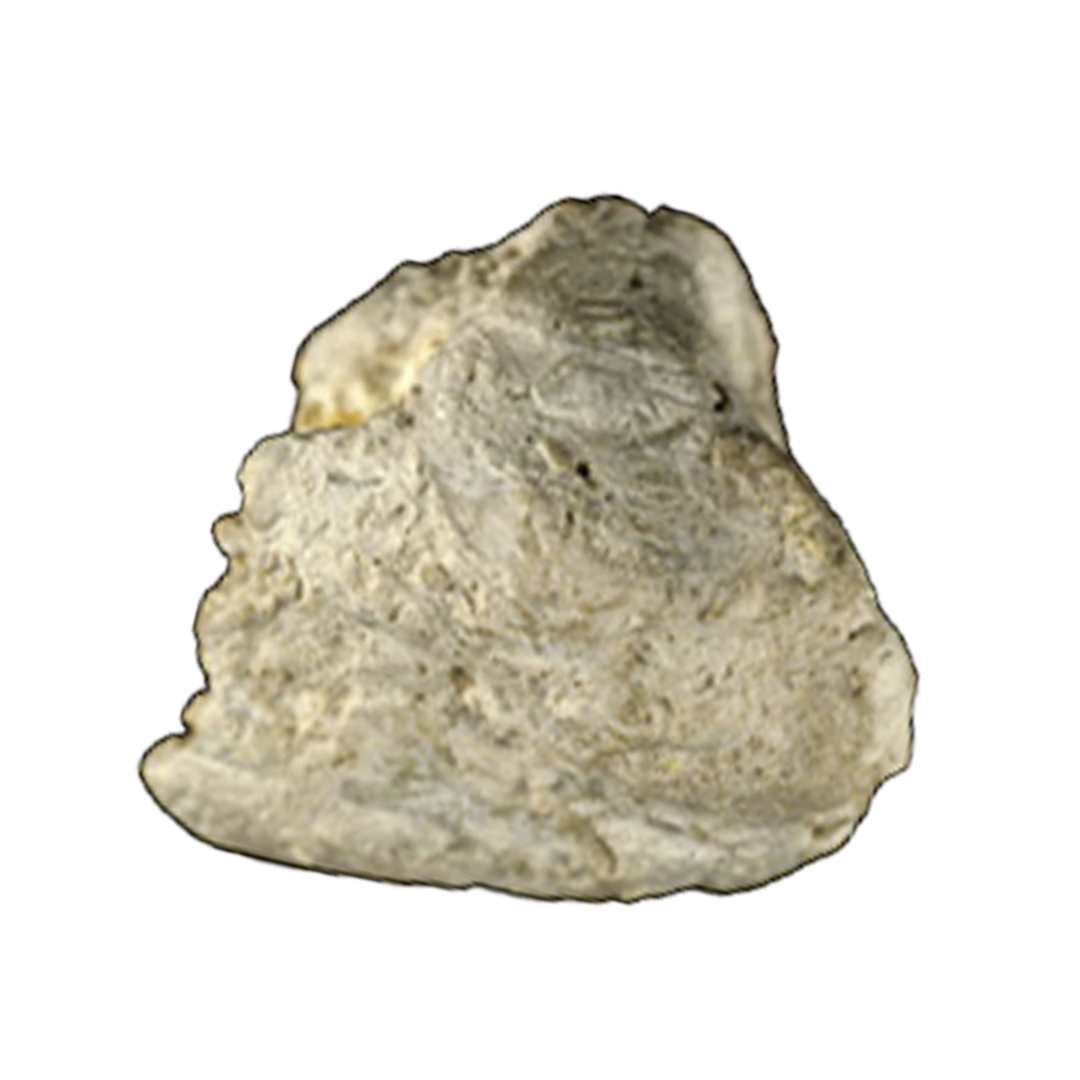

TYPE IIId STONES
These stones have the following:
- Uneven, rough and porous surface
- Grayish to dark brown color
These stones form due to chronic diarrhea, electrolyte/alkali loss, high urate (uric acid salt) concentration in urine, low phosphate intake, or laxative abuse (medications for loosening stool).
Aside from these four, there are also mixed uric acid and calcium-oxalate stones. These mixed stones form when you have risk factors for both types. They are typically observed in individuals who are obese. They are especially severe and recurrent. Since we only covered UA stones in this blog, we suggest that you also dive into our Calcium Oxalate Stone Blog to know the risk factors for this type.
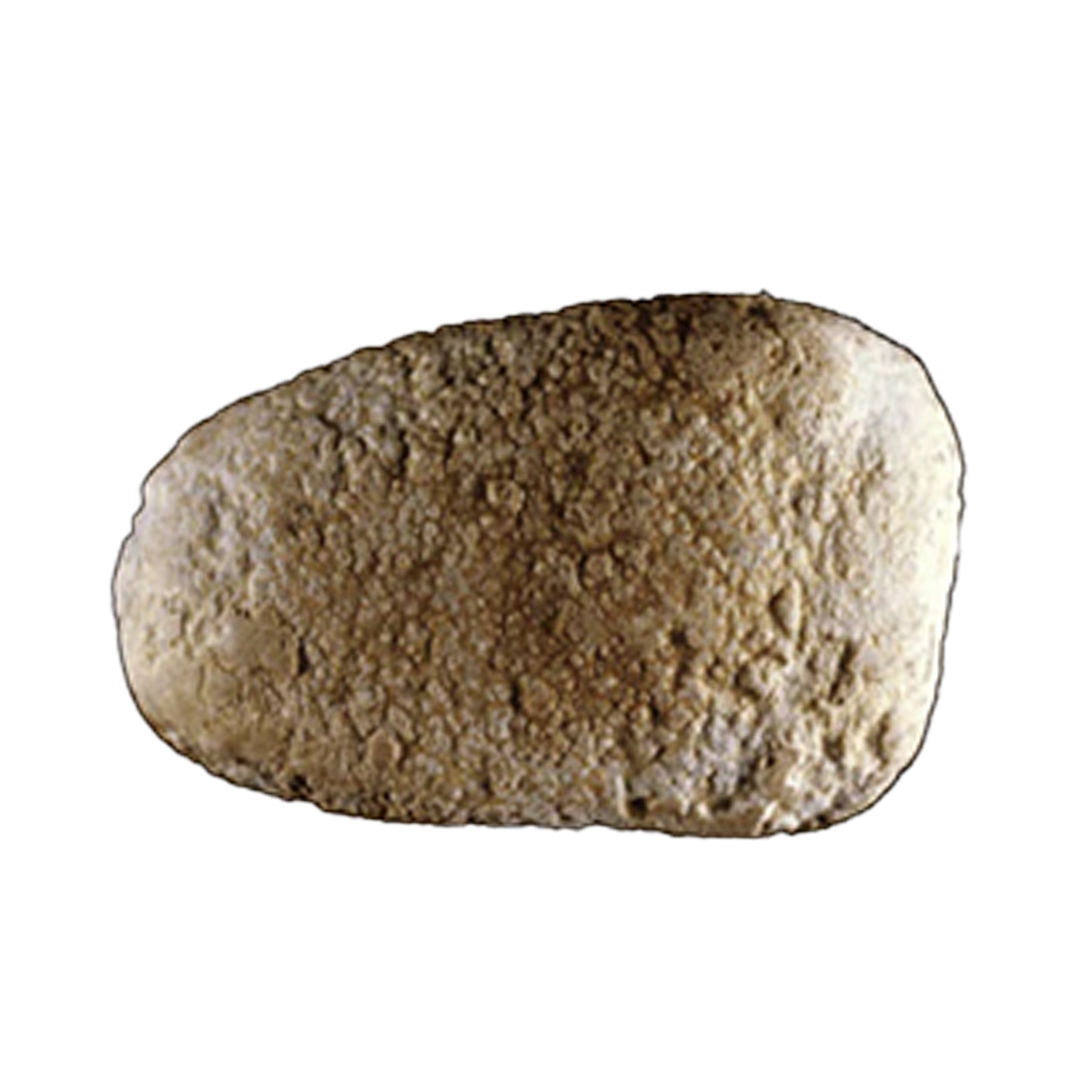

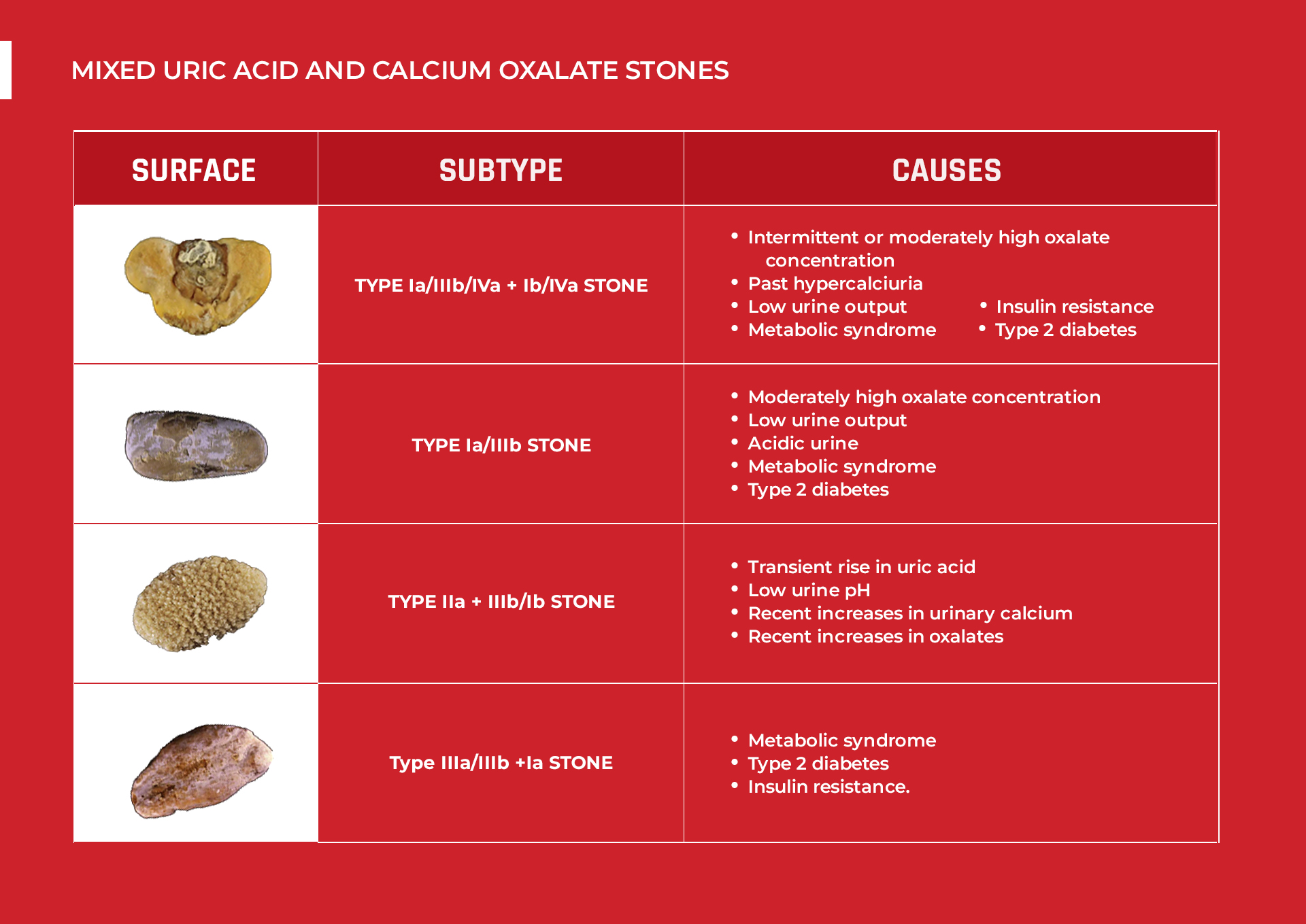
TYPE Ia/IIIb/IVa + Ib/IVa STONE
This type is characterized as follows:
- Smooth surface
- Has a prominent umbilication
- Has yellowish to brownish color
Underneath this yellowish surface, you will notice a whitish internal structure with brownish lines (somehow like rings). There are also patches of black.
These stones form due to intermittent (on and off) or moderately high oxalate concentration and past hypercalciuria (excess urinary calcium). These are in addition to UA stone risk factors such as low urine output, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes.
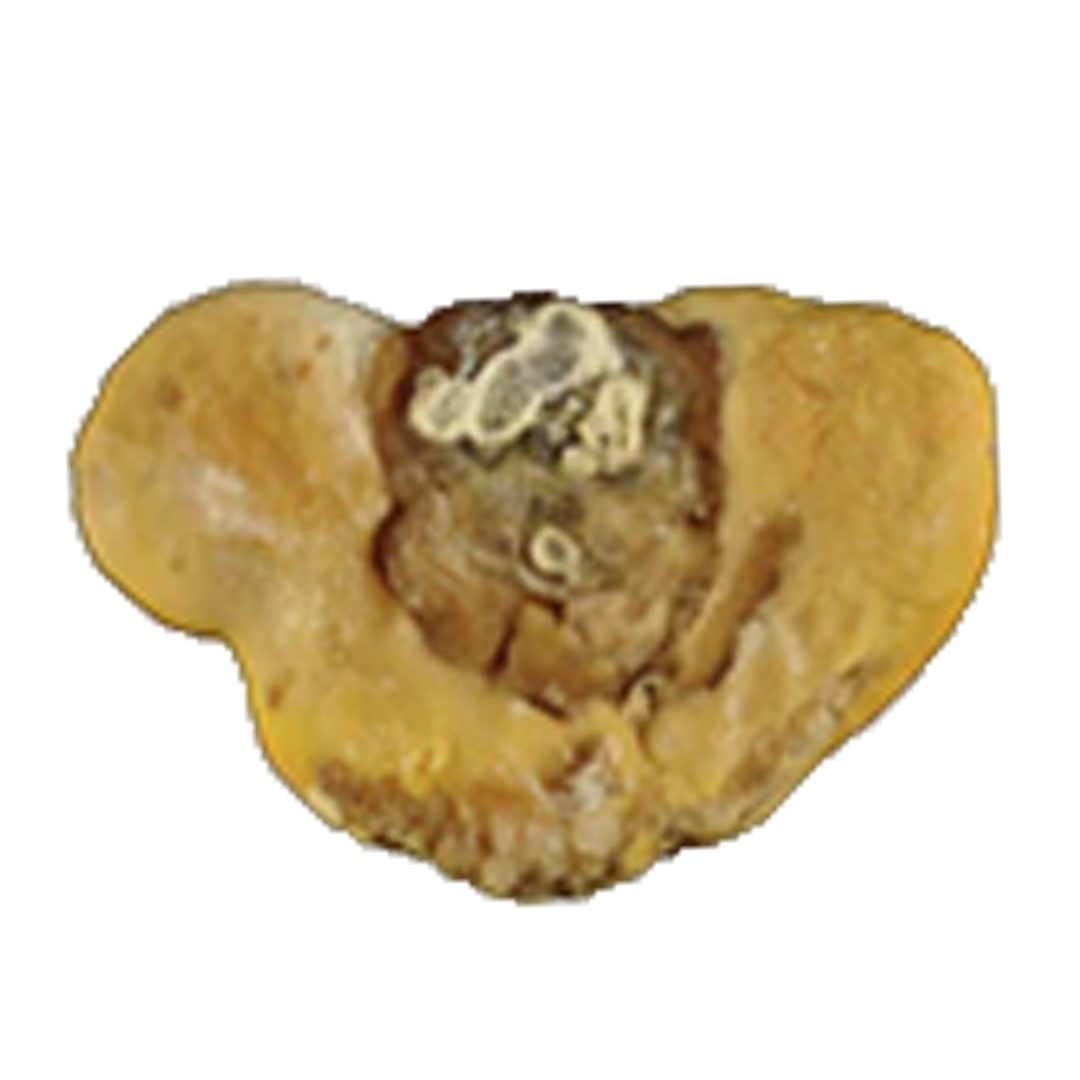

TYPE Ia/IIIb STONE
These stones have embossed yellowish or brownish layers that are unevenly distributed against the white and brown surface.
Inside, you will notice some layers that are dark brown to black in color. These irregularities in texture and hue are due to moderately high oxalate concentration, low urine output, acidic urine, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes.

TYPE IIa + IIIb/Ib STONE
These stones have these attributes:
- Spiky but less prickly surface
- Light to yellowish color
The internal structure shows concentric layers of brown and black. This signals a transient rise in uric acid and/or low urine pH, plus recent increases in urinary calcium and oxalates.
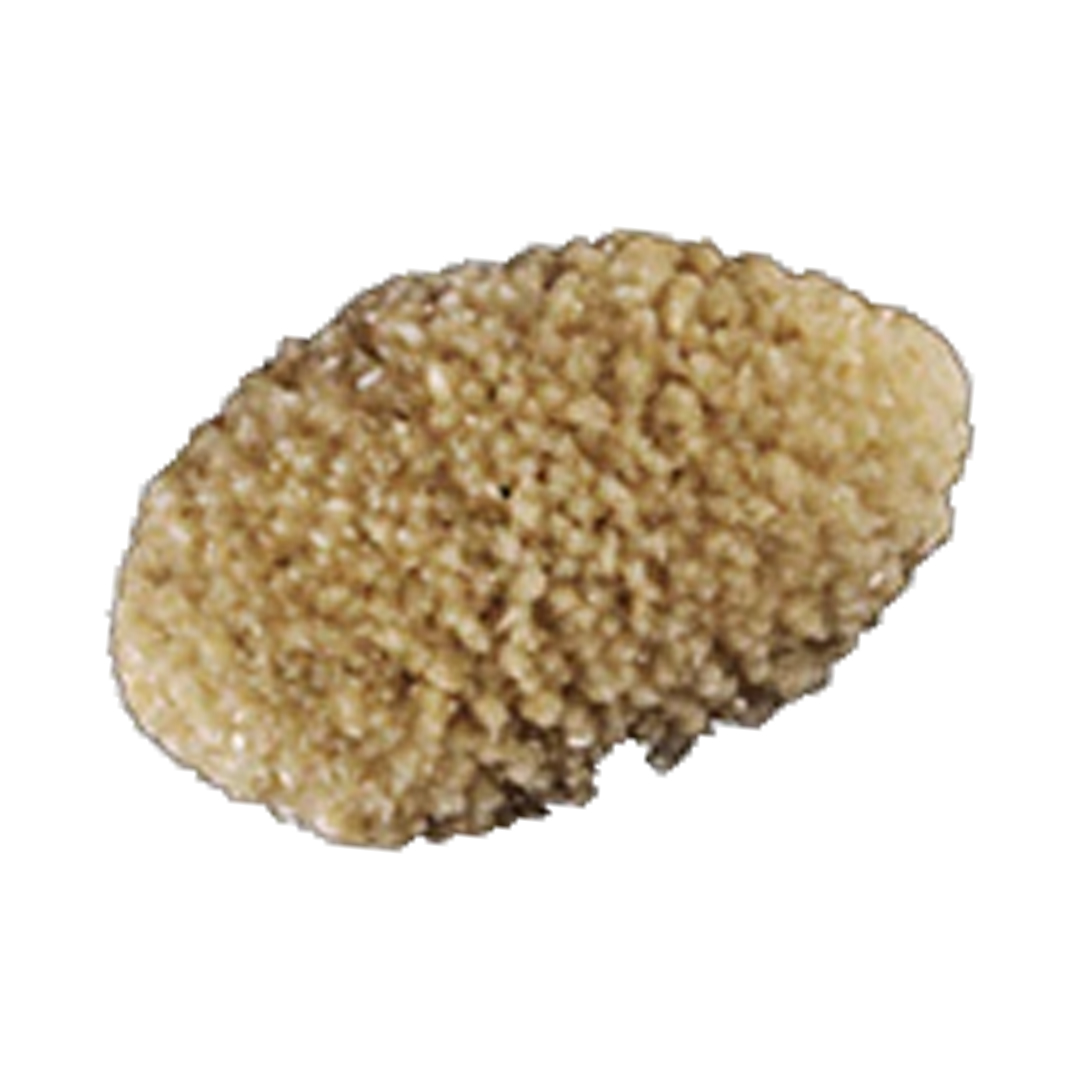

TYPE IIIa/IIIb +Ia STONE
This type has the following:
- Slightly rough surface
- Has white color with patches of orange or orange-brown
These stones have a brown internal structure and a prominent black core. These stones form primarily due to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, or insulin resistance.
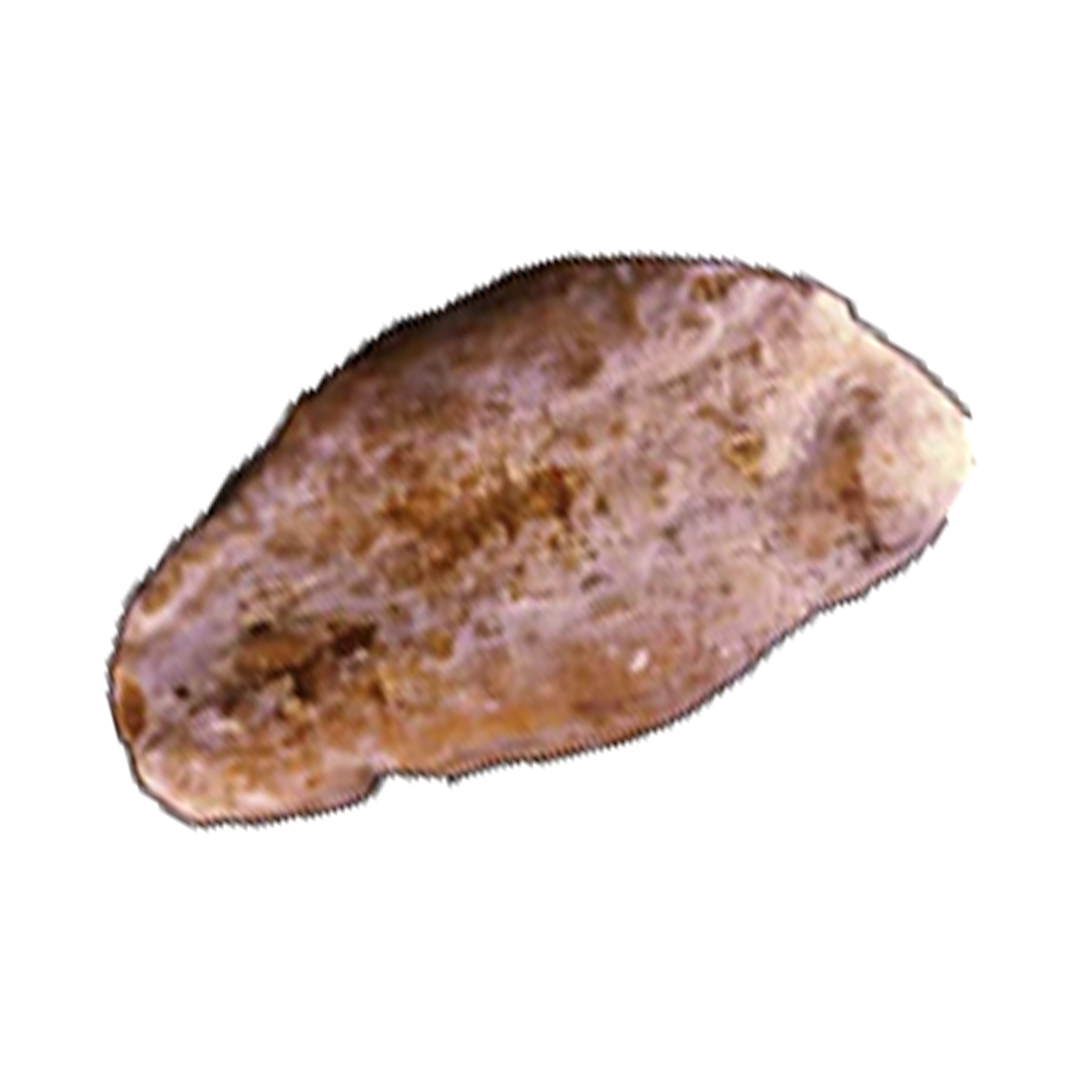

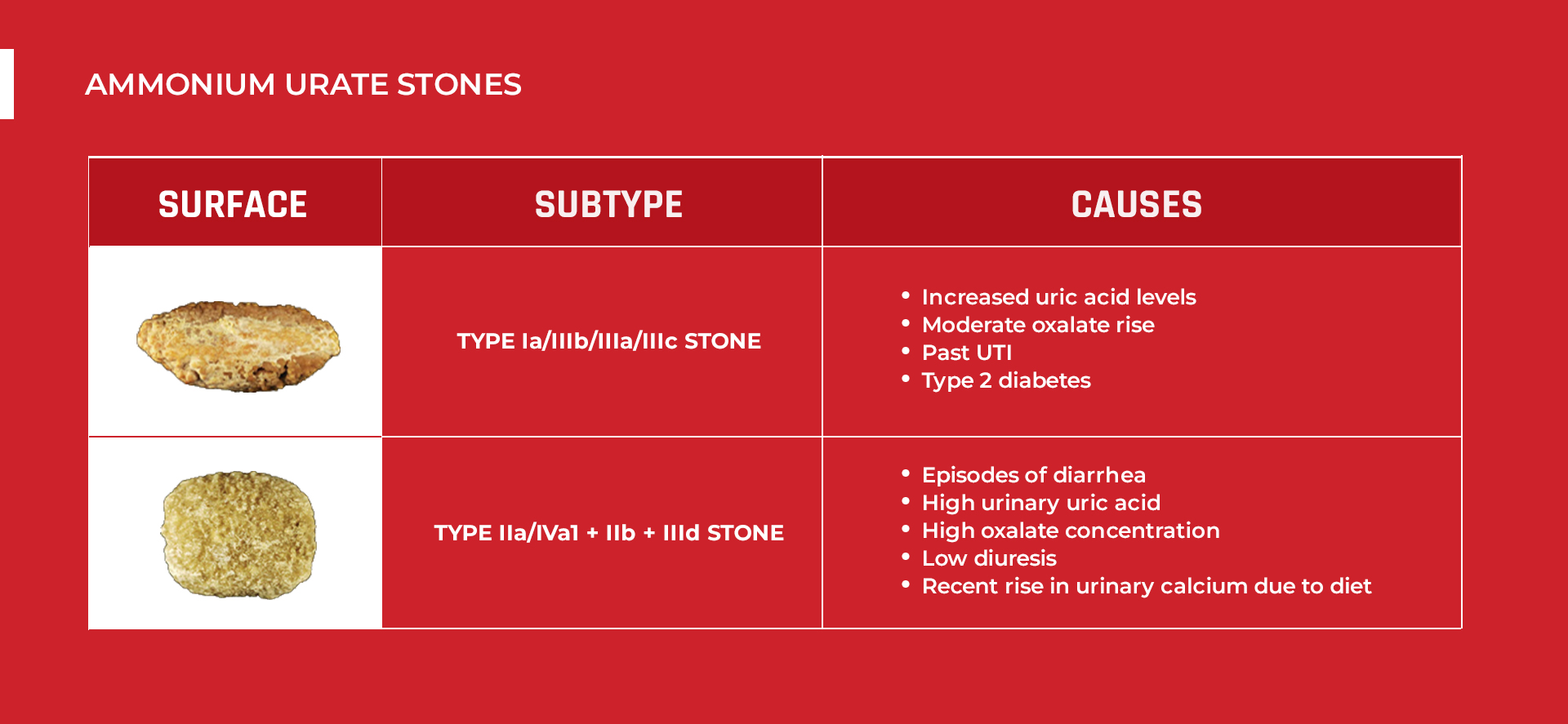
Another sub-category of UA stones are ammonium urate stones. Although they account for less than 0/4% of all kidney stones, interestingly, they are frequent in regions such as Africa and Southeast Asia. They have two different forms:
TYPE Ia/IIIb/IIIa/IIIc STONE
This subtype is characterized as follows:
- Having a rather smooth but blistery-like surface
- Light yellow to light brown in color
This type has three layers: the yellowish surface, the black middle layer, and the whitish core. This distinctive appearance is due to increased uric acid levels, a moderate oxalate rise, and past urinary tract infections or type 2 diabetes.

TYPE IIa/IVa1 + IIb + IIId STONE
These stones are characterized by:
- Rough surface
- Light yellow color
Internally, these stones have a brownish-yellow color with concentric layers, usually with lines of black. This results from episodes of diarrhea, high urinary uric acid, high oxalate concentration, low diuresis, and a recent rise in urinary calcium of dietary origin.

HOW TO MANAGE URIC ACID KIDNEY STONES
Treating UA stones isn’t as complicated as most people think. Honestly, for most individuals who form this type, surgery is almost unnecessary. This must be surprising on your part, but that’s the truth. Uric acid stones are weak-density stones. Meaning they can easily break apart while still inside the urinary tract. Some potent natural supplements, like CLEANSE, contain stone-breaking properties to do the job. Taking CLEANSE will not only help you break your UA stone but also to pass them smoothly. That’s because it has pain relief, anti-inflammatory, diuretic and stone-breaking ingredients.
On the prevention side, you can check out our Coaching Program. In this program, we will help you formulate a personalized strategy on how to combat uric acid stones effectively. See you there!
References
- Comprehensive morpho-constitutional analysis of urinary stones improves etiological diagnosis and therapeutic strategy of nephrolithiasis
- The influence of metabolic syndrome and its components on the development of nephrolithiasis
- Diabetes mellitus and the risk of nephrolithiasis
- Uric Acid Stones and Hyperuricosuria

Comments or questions?
Responses
WHAT TO READ NEXT
Publish Date: August 18, 2024
Staghorn Kidney Stones Are BIG Problems!
Publish Date: August 4, 2024
Brushite Stones: The Most Complex Kidney Stones
Publish Date: July 28, 2024
The Deadly Struvite Stones